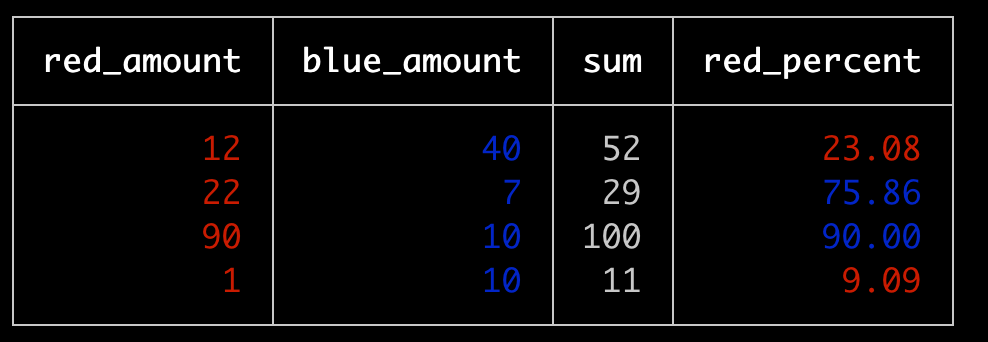
Calculated Columns
Sometimes you need a new column added automatically whose val is dependent on other fields in the same row.
Basic Example
import { Table } from 'console-table-printer';
const chalk = require("chalk");
const p = new Table({
columns: [
{ name: "red_amount", color: "red" },
{ name: "blue_amount", color: "blue" },
],
computedColumns: [
// creating new columns based on other column vals
{
name: "sum",
function: (row) => row.red_amount + row.blue_amount,
},
{
name: "red_percent",
function: (row) => {
const val = ((row.red_amount / row.sum) * 100).toFixed(2);
if (val <= 50) {
return chalk.red(val);
}
return chalk.blue(val);
},
},
],
});
// add rows
p.addRows([
{
red_amount: 12,
blue_amount: 40,
},
{
red_amount: 22,
blue_amount: 7,
},
{
red_amount: 90,
blue_amount: 10,
},
{
red_amount: 1,
blue_amount: 10,
},
]);
// print
p.printTable();
Using All Parameters
The computed column function can take three parameters:
row: The current row dataindex: The current row number (starting from 0)array: All rows in the table
Here's a simple example showing how to use each parameter:
import { Table } from 'console-table-printer';
const p = new Table({
columns: [
{ name: "name" },
{ name: "score" }
],
computedColumns: [
// Using row: Get pass/fail status
{
name: "status",
function: (row) => row.score >= 60 ? "PASS" : "FAIL"
},
// Using index: Add row numbers
{
name: "student_no",
function: (row, index) => `Student #${index + 1}`
},
// Using array: Compare with class average
{
name: "vs_average",
function: (row, index, array) => {
const avg = array.reduce((sum, r) => sum + r.score, 0) / array.length;
return row.score > avg ? "Above Average" : "Below Average";
}
}
]
});
// add rows
p.addRows([
{ name: "Alice", score: 85 },
{ name: "Bob", score: 55 },
{ name: "Charlie", score: 70 },
{ name: "David", score: 65 }
]);
// print
p.printTable();
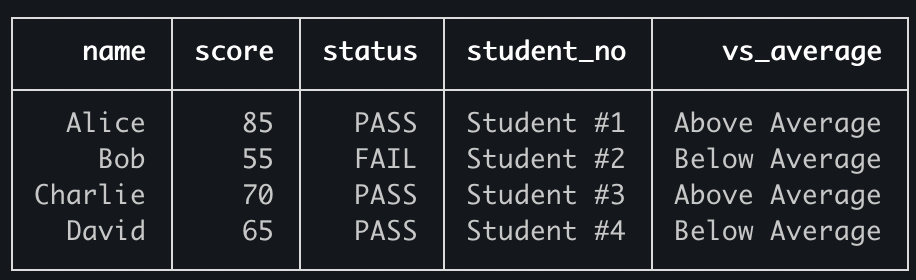
This example shows:
- Using
rowto check if a student passed - Using
indexto add student numbers - Using
arrayto compare scores with class average
The output will show each student's score, their pass/fail status, student number, and how they compare to the class average.
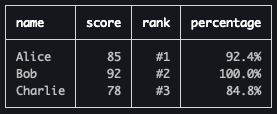
Advanced Examples
Using Row Index for Ranking
import { Table } from 'console-table-printer';
const table = new Table({
columns: [
{ name: "name", alignment: "left" },
{ name: "score", alignment: "right" }
],
computedColumns: [
{
name: "rank",
function: (row, index) => `#${index + 1}`
},
{
name: "percentage",
function: (row, index, array) => {
const maxScore = Math.max(...array.map(r => r.score));
return `${((row.score / maxScore) * 100).toFixed(1)}%`;
}
}
]
});
table.addRows([
{ name: "Alice", score: 85 },
{ name: "Bob", score: 92 },
{ name: "Charlie", score: 78 }
]);
table.printTable();
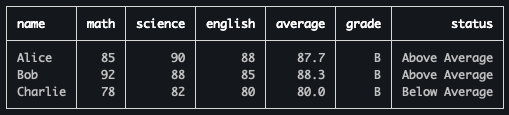
Complex Computations with Multiple Subjects
import { Table } from 'console-table-printer';
const table = new Table({
columns: [
{ name: "name", alignment: "left" },
{ name: "math", alignment: "right" },
{ name: "science", alignment: "right" },
{ name: "english", alignment: "right" }
],
computedColumns: [
{
name: "average",
function: (row) => {
const scores = [row.math, row.science, row.english];
return (scores.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0) / scores.length).toFixed(1);
}
},
{
name: "grade",
function: (row) => {
const avg = parseFloat(row.average);
if (avg >= 90) return "A";
if (avg >= 80) return "B";
if (avg >= 70) return "C";
if (avg >= 60) return "D";
return "F";
}
},
{
name: "status",
function: (row, index, array) => {
const avg = parseFloat(row.average);
const classAvg = array.reduce((sum, r) => sum + parseFloat(r.average), 0) / array.length;
return avg > classAvg ? "Above Average" : "Below Average";
}
}
]
});
table.addRows([
{ name: "Alice", math: 85, science: 90, english: 88 },
{ name: "Bob", math: 92, science: 88, english: 85 },
{ name: "Charlie", math: 78, science: 82, english: 80 }
]);
table.printTable();